Postmates Business Model & Revenue Model
Discover how Postmates works and makes money! Delve into their business and revenue models to understand how this on-demand delivery service operates.
Postmates, An Overview
Postmates is a popular third-party delivery service that was founded in 2011 and acquired by Uber Technologies, Inc. It is headquartered in San Francisco, California. and it is operational in about 3,000 cities across the United States.
Postmates was initially operating as a local courier service that provided people with extra capacity in their cars to make deliveries. Soon, it evolved to become a platform that would make on-demand deliveries of food and other goods.
With the help of the Postmates platform, a person can browse through a variety of stores, order the things they like, and have them delivered to their desired location.
The platform connects people with retail merchants and delivery partners. In exchange for its services, Postmates obtains a commission from the users and the retail merchants. The delivery partners are compensated by the company for helping with the delivery.
What makes the app most appealing is that, unlike other on-demand delivery platforms that mostly focus on food deliveries, Postmates’ services extend beyond restaurants. It's the platform for all kinds of necessities, from groceries to pharmaceuticals to a variety of other commodities, and they are delivered within minutes, if not hours, of placing the order.
Postmates, which is recognised as one of the pioneers in the on-demand industry, is also a major player in the business, competing with names such as GrubHub, DoorDash, and another Uber subsidiary, Uber Eats.
The Customer Segments That Postmates Serve
Postmates, as an on-demand delivery service platform, targets three groups of people who can benefit from their business model. By serving these people, Postmates runs its business and makes revenue out of it. Let's find out who they are.
Users
Users of Postmates are people who are either too busy to go shopping or don't have much time to go out due to many reasons. Or they may, in plain language, prefer to stay at home instead of going out to eat or shop for things.
These people are ready to pay an extra fee to receive food, groceries, and many other things at their doorstep.
Retail Merchants
Retail merchants are store owners who sell a variety of things, from pharmaceuticals to instant dinners. fresh food, vegetables, dairy, and so on.
These people wish to expand their customer base by making door deliveries and advertising in places where they can get the attention of potential customers.
Delivery Providers
Students who want to work part-time or people who have a full-time job but wish to supplement their income by making deliveries in their free time as a side hustle can become delivery providers.
People who are unemployed and wish to earn money by making deliveries can also become delivery providers, part-time or full-time.
By becoming delivery providers, these people get paid for each delivery they make and earn money at their own pace.
The Functioning of Postmates
The Postmates business model is straightforward. Customers place orders from local retail stores using the Postmates platform. The retail stores prepare the order, and the firm uses a fleet of delivery partners to deliver these orders from local merchants to customers. These delivery partners pick up orders from stores and deliver them to customers.
Postmates earns its revenue by charging delivery fees and service fees to users for each order. Postmates also charges retailers a commission on each order they complete which adds to its revenue. Let's see the business model in detail
The business model of Postmates
The business model of Postmates links the user with local retailers at first. Postmates allows users to browse through the many stores on the platform and order anything from the menus.
User end
-
The user places the desired item in the cart and confirms the order. The user can choose to have the item delivered to their desired location for an extra delivery fee or to collect it from the store themselves.
-
When it comes to paying for delivery, the user has multiple options, and they can choose to pay for the order when they place it or they can pay when it is delivered.
-
The user can also track the order until it is delivered.
-
Once the user receives their delivery, they rate their order as well as the delivery experience on the platform.
Merchant’s end
-
When the users place the order, the store is notified of the order, and they start preparing the order for delivery or takeaway.
-
Once the order is ready to be collected, the store requests a delivery provider through Postmates’ platform.
-
After the delivery partner arrives, they confirm the order number with the delivery partner, and they hand it over to them.
Delivery partner’s end
-
The delivery partners who are close to the said store are notified when a delivery request is made, which they can choose to accept or decline. When one delivery partner rejects the request, it is passed on to another.
-
When a delivery partner accepts the request, they are given the order number and order details. They can now go to the store and pick up their order.
-
Once they give the store person the order number, they can get the order from the store and start driving to the delivery location.
-
After the delivery partner reaches the user’s location, they deliver the order and receive the order total. If the total has already been paid, they deliver the order and leave.
The expense structure of Postmates
Postmates’ expenses are mostly concerned with the maintenance and development of its technology platform. The platform is frequently updated to improve the user experience, thereby increasing customer satisfaction.
The cost structure of Postmates also includes the salaries of its full-time employees as well as the payments made to its delivery partners.
Insurance, running costs, and all other minor expenses are also included in the expense structure of Postmates.
The revenue streams of Postmates
Postmates' revenue is not limited to commissions from retail partners or service fees charged to users. Postmates earns revenue through various other channels, which include:
i. Delivery fee:
Postmates charges a minimal delivery fee for each order processed. However, 80% of this total delivery fee goes to the delivery guy, with the other 20% being retained by Postmates.
ii. Convenience fee:
Aside from the delivery cost, Postmates charges its customers a flat fee of 9% on each order as a convenience fee. Customers are also willing to pay this fee as they consider that it is easier to have things delivered to their door than to go out themselves, wasting time and gas.
iii. Increased Prices:
Many on-demand startups employ a unique pricing algorithm to increase expenses when demand surpasses online delivery supply. Postmates, too, uses a similar feature that creates a strong financial incentive to be available when it is most required.
iv. Postmates Unlimited:
The firm also introduced a subscription service structure into its business model. With this programme, the members will not be charged a service fee on any of their orders or be impacted by surge pricing.
The members also receive occasional perks, and for this, people are willing to pay for the membership. This adds to the revenue of the platform.
What Does Postmates Do?
The fundamental activities that Postmates does are fulfilling the orders placed by its users and maintaining good relationships with retail merchant partners to ensure the smooth operation of the company and its services.
Recruiting delivery partners is another important activity of Postmates, as it is important to have a huge fleet of delivery partners to serve a large number of customers on demand.
Customer acquisition and maintaining the technological infrastructure are other important activities undertaken by Postmates.
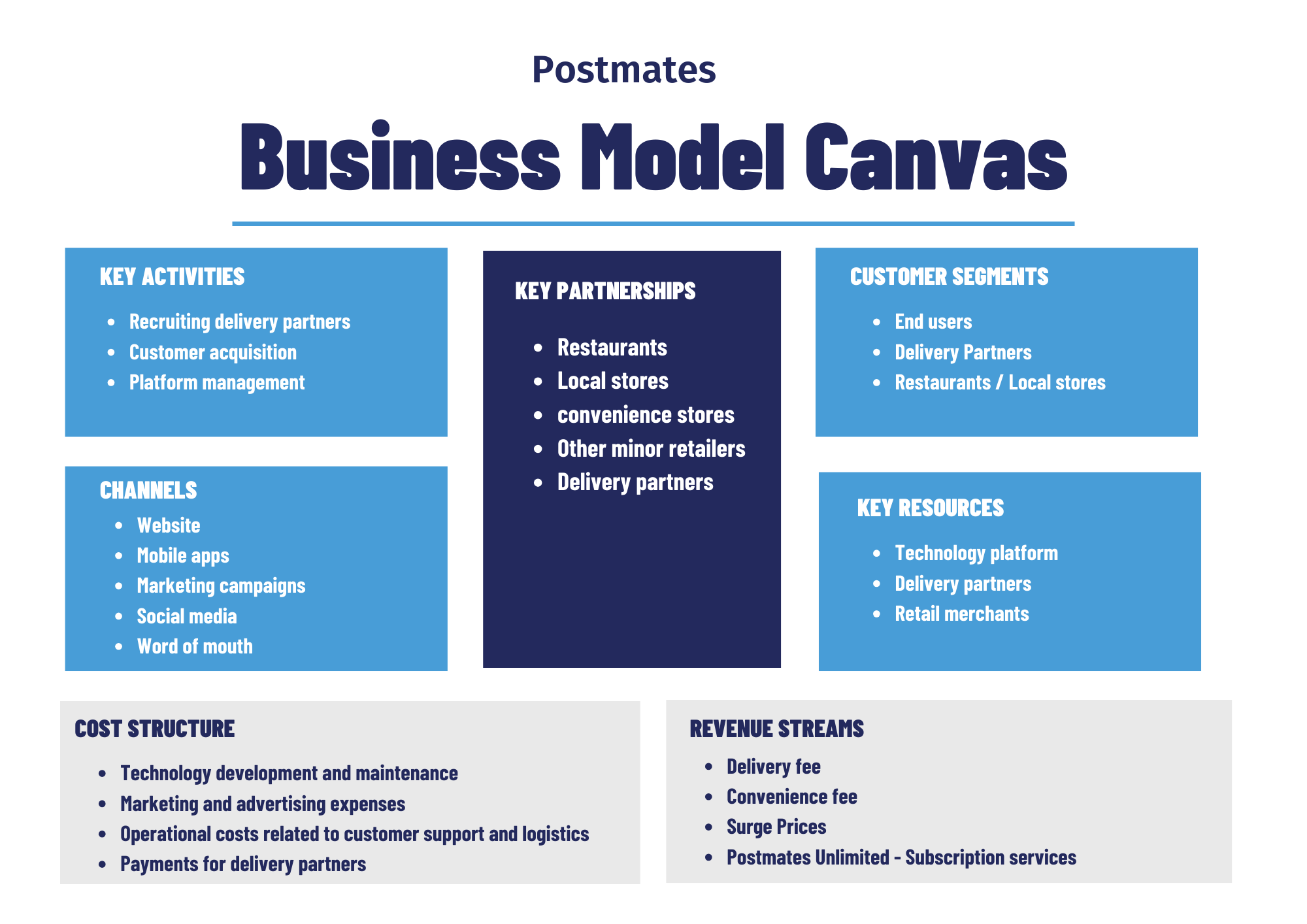
The Factors That Keep Postmates’ Business Running
Postmates can provide the service and keep operating its business, thanks to the people and the resources they work with. It is with the help of these resources and their partners that they can deliver a value proposition to the users.
Key partners of Postmates
Naturally, as a platform that handles on-demand goods delivery, the supply side, i.e., restaurants, local stores, and other minor retailers, are the prominent partners that give them business. Its delivery service providers, who bring customers their orders, are also considered partners on the platform.
Recently, Postmates released an API that allows businesses like Starbucks, Target, and Instacart to incorporate Postmates into their applications and use Postmates' fleet to deliver items in Postmates' geographical areas. Through this arrangement, Postmates can partner with some big names among the retail chains as well.
Key resources of Postmates
The delivery partners:
The fleet of delivery partners is considered a main resource of the platform, as they make all the deliveries on the orders made through the platform. Without a large number of delivery partners, Postmates cannot serve as effectively as it does.
The partnership with retail merchants:
Its partnership with local restaurants, convenience stores, and other retailers is another important resource for the business, as it serves as the supply side of the business.
The technology platform:
Postmates’ technological platform is critical for all communication and transactions between its three customer segments, so the platform is also an important resource for the business.
The Value Propositions Offered To The Customers Of Postmates
Postmates offers an attractive value proposition for each of its customer segments. The value propositions satisfy the needs of each of its three customer divisions in many ways. Let's examine them separately.
Value Proposition for Users
The first key value proposition offered to the user segment is that the user can order a large variety of goods from any local retailer on the platform.
The service of Postmates is available around the clock. Users can place orders even at midnight, as long as the stores are open.
The platform also offers speedy delivery of goods in as little as an hour or two while enabling its users to also track the status of their order.
The Value Proposition for Retailers
Postmates is partnered with a variety of retailers, from convenience stores to local eateries and vegetable vendors. As a result of this arrangement, the retail stores listed on the platform are exposed to the customers of the other stores on the platform.
For retailers, this extensive exposure becomes a beneficial advertising channel that draws in many new customers, which is Postmates’ first value proposition to its retailer segment.
Another value proposition presented to retailers is that they can serve customers who prefer to get deliveries without hiring and paying a delivery person themselves.
By partnering with Postmates, retailers can hire a delivery person to make the delivery, and the customer will pay the delivery fee themselves.
The Value Proposition for Delivery Partners
The main value proposition of Postmates to its delivery partners is that they can conveniently choose when they work.
Since the delivery partners of Postmates are paid for each delivery they make individually, they can choose to work at their will, and they will get paid accordingly.
This flexibility in the work schedule comes to the advantage of students who work part-time or even people who work other jobs, as they can make it a side hustle to make deliveries in their free hours for a little extra money.
How Postmates Reaches Its Target Audience
In the initial days, Postmates made use of all the methods at their disposal, such as digital marketing, offline advertisements, promotions, and every other marketing option, to get the attention of their target audience.
Once Postmates reached its initial audience, it was word of mouth that had been their most beneficial channel. Word of mouth had been an effective marketing channel that ensured the authenticity of Postmates’ services to its potential customers. This helped the business reach more people and expand its services further.
Is Postmates’ Business Model Successful?
Soon after Postmates was launched in 2011, it became an immense success as the platform extensively utilised social media to engage directly with its users and by providing outstanding online support to its customer segments. Postmates found a loyal customer base in a short period of four years, which they were able to achieve by absorbing feedback and ratings and rectifying their issues.
The innovative business model of Postmates helped the company build a broad base of customers in a very short time, and Postmates was able to officially tie up with Apple, McDonald's, Starbucks, Walgreens, Chipotle, and a vast variety of other prominent businesses through the success of its business model.
The firm also profited immensely from the new leadership following Uber's acquisition of Postmates in 2020, as it continued to develop during the period. Through this acquisition, Postmates and Uber Eats collaborated and exchanged resources and technology to connect with a wider consumer base in a simple and cost-effective way, which increased efficiency, its most recent and apparent depiction being the development of delivery robots. As a result, it is safe to infer that the platform has seen great success with its current business strategy and will continue to grow in the future.





