Uber Eats Business and Revenue Model
Unveiling the Uber Eats business and revenue model: Exploring the innovative strategies driving its success in the food delivery industry.
Getting things delivered is a typical occurrence these days, especially in light of the global pandemic that forced us all to become familiar with all of the delivery options accessible to us, food being a popular one among them.
Merely a handful of food delivery businesses operate on an international scale, and Uber Eats is one of the most well-known of them.
By browsing through all the restaurants listed on the platform, the customer can find and order food from any restaurant they want and have it delivered to their preferred location.
A delivery person then brings the order to the said location. The customer either chooses to pay when placing the order or chooses to pay on delivery.
For the end user, the procedure is straightforward, yet there is a lot that goes on in the background of the application of which they are largely unaware, such as the delivery partners assigned by the system, the ties it has with the restaurants or the kind of transactions that occur between them.
In the following sections, we shall take a look at Uber Eats' business and revenue models to gain an understanding of how the app and the company that runs it operate.
The Business Model of Uber Eats
Food delivery applications like Uber Eats use a three-way mediation approach that links customers with restaurants and these two with delivery partners.
When a customer places an order through the Uber Eats application, the restaurant is notified of the order and is instigated to prepare the food.
The application assists with assigning a delivery partner to pick up the order from the restaurant and deliver it to the customer’s desired location.
In this triangle model, the customer pays the restaurant for the food, then pays the delivery partner the delivery cost, and also pays the app an additional service charge.
As a service charge, the restaurants also pay Uber Eats a commission on each order received through the app.
In addition, Uber Eats deducts a portion of the delivery charge as a commission before paying the delivery partners according to the number of deliveries they completed and the distance they had travelled. On the Uber Eats platform, transactions happen in this manner.
Let's now examine Uber Eats' business model canvas to gain a better grasp of how the company behind the app operates.
Key partners
The factors that build a firm from the ground up are its partners. Some of the most significant transactions necessary for the smooth operation of a business are carried out between a specific firm and its key partners.
And when it comes to Uber Eats, it goes without saying that neighbourhood restaurants and delivery providers are its main business partners.
Uber Eats' value proposition to its end users is that the platform allows them to order food from the range of listed restaurants from the convenience of their home, and have the food delivered to the customer, fresh, and within minutes to their doorstep.
In order to be able to deliver this value proposition to the customers, it is critical that Uber Eats is partnered with as many local restaurants as possible. By partnering with a number of restaurants, the platform could offer a variety of cuisines in the locality and keep themselves relevant in the food delivery industry.
Also by partnering with Uber Eats, the restaurants gain from the arrangement as it helps them serve an extended customer base by making deliveries which brings in more business and sales. For this reason, the restaurants are a key partner to Uber Eats’ business.
Delivery partners are independent contractors who are also important to the company since without them, it could only service take-away customers, which would have a significant negative impact on its business.
Uber Eats is also reliant on its investors to keep its business and application running smoothly.
Key Resources
The Uber Eats website and mobile app serve as the means by which the separate entities of customer segments are connected to one another and, ultimately, to the company.
Uber Eats' platform is a crucial resource for the company since it is essential for the company to operate as a business.
In an objective sense, Uber Eats' affiliations with neighbourhood restaurants and its staff of both full-time and freelance delivery drivers are also regarded as important assets for the company.
Key Activities
UberEats' top priorities may be divided into three categories: platform management, customer acquisition, and building partnerships.
Uber Eats' primary focus is on managing and maintaining its technological platform, which is an essential resource for the company and is updated frequently to meet customer needs.
Maintaining productive connections with its delivery and restaurant partners is another crucial task that Uber Eats undertakes to keep its business running properly and to draw in new partners.
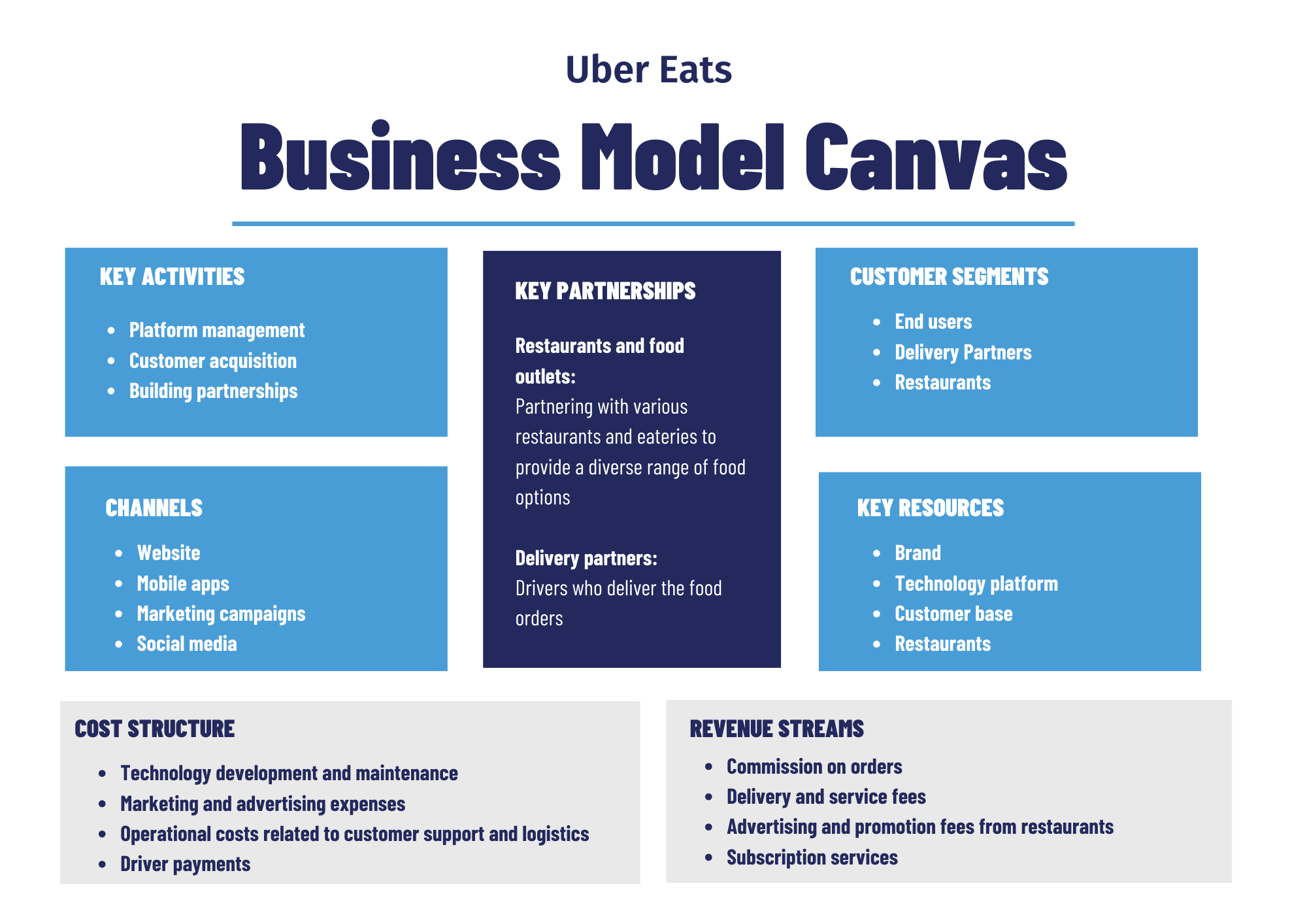
Customer Segments
It is quite obvious that the customer segment of Uber Eats’ business model is made up of these three entities: the end users, the restaurant partners and delivery providers.
End users: This could be people who can't cook or people who do not feel like cooking on particular days but don't want to go out and get food either. It could also be people who are just craving an unusual cuisine and want to try it in the comfort of their own homes. These are the people who benefit from using the application.
Local restaurants: These are the neighbourhood restaurants that are willing to increase their customer base by offering deliveries but do not have the resources to do so. They benefit from the orders the platform brings them, to whom they can provide delivery service without having to hire a delivery person themselves.
The delivery providers: These are the individuals who are looking to enhance their income and are willing to make deliveries part-time or full-time. These individuals are self-employed, as they work at their own convenience and get paid for each delivery they make shortly after the work is completed.
Value Proposition
For each of its customer segments, the platform provides a distinct value proposition, which is as follows:
End users:
A great deal of restaurants are made accessible to the end user who registers with Uber Eats. With just a click, they may also obtain details about the anticipated delivery timings and access delivery tracking. End users can also choose from a variety of payment methods.
Partner restaurants:
Uber Eats offers delivery services, which help its partner restaurants expand their customer base by hiring delivery drivers. Listing themselves on Uber Eats is another way for restaurants to market their businesses effectively.
Delivery partners:
These delivery partners are able to supplement their income by using Uber Eats, as the platform enables them to work at their convenience. Likewise, depending on the location, the Uber Eats platform presents delivery partners with the option to select the vehicle they would prefer to use, which might be a car, motorcycle, or even a bicycle.
Channels
The Uber Eats website, together with its iOS and Android apps, are regarded as the platform's most effective channels. Word of mouth and significant monetary incentives, such as discounts and credit for future orders, are also some other effective channels of the business.
The Revenue Model of Uber Eats
The revenue model of Uber Eats takes into consideration the company's revenue streams as well as the expenses related to operating this online platform for food delivery from third parties. Let's examine them in more detail.
Revenue Streams
The revenue that Uber Eats generates comes from a variety of sources. The following are a few of them:
Commission on orders:
Every order placed through the Uber Eats platform results in a commission being charged to the partner restaurant. Although it can vary, this commission usually consists of 15% to 30% of the order amount. This commission, which the partner restaurants pay the platform, is its primary source of income.
Delivery and Service fee:
The cost of the delivery service is borne by the customer and varies according to demand, distance, and locality; a percentage of this cost serves as revenue for Uber Eats. Additionally, users contribute to the company's earnings by paying a service fee for using the application.
Advertising and Promotions:
Through the platform’s advertising and promotional services, Uber Eats gives restaurants the opportunity to highlight their listings. Restaurants can increase their visibility on the site by paying for these extra features. This increases Uber Eats' revenue as well.
Subscription Services:
Uber Eats provides subscription services similar to Eats Pass in certain markets. A monthly subscription fee is paid by subscribers in exchange for perks like free shipping and savings. This revenue from subscriptions is an extra source of income for the platform.
Cost Structure
The primary focus of Uber Eats' cost structure is platform maintenance, which is also where the company's primary revenue comes from, coupled with marketing and customer acquisition (CAC) costs.
Uber Eats' cost structure also covers the payments made to its full-time employees as well as its independent delivery partners.
The costs associated with credit cards, legal fees, R&D, customer assistance, and other responsibilities are also included in the company's cost structure, and there you have it: the revenue model of Uber Eats.
Summing up:
As we can observe, the platform of Uber Eats is what ties delivery partners, restaurants, and end customers together and then connects them all to the company itself.
As a result, the platform serves as the foundation of the company's operations and revenue models, allowing for highly efficient operations, which inspires many to get involved in the third-party food delivery business.





